Chapter 6
Strategic Steps for Implementing Smart Supply Chain
"The future of supply chains lies in industry-specific innovations powered by AI, IoT, and automation, allowing businesses to stay competitive and agile in a rapidly changing global landscape." — Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft.
Chapter 6 focuses on the industry-specific innovations driving the transformation of smart supply chains in key sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, logistics, and energy. It highlights how technologies like Industry 4.0, AI, IoT, and blockchain are being applied to create smart factories, optimize cold chain management, enable real-time fulfillment, and improve logistics efficiency. The chapter also delves into the importance of smart grid systems and AI-driven resource management in the energy sector, showing how these innovations are streamlining operations, reducing waste, and enhancing overall supply chain resilience.
6.1. Manufacturing 4.0 and Smart Factories
Industry 4.0 represents the fourth industrial revolution, a major shift in manufacturing that integrates advanced digital technologies into traditional production systems to create highly interconnected and autonomous smart factories. Recent studies emphasize the potential of Industry 4.0 to improve operational efficiency, enhance resilience, and promote sustainable practices in manufacturing (Kamble, Gunasekaran, and Dhone, 2020; Deloitte, 2021). Characterized by the convergence of IoT (Internet of Things), AI (Artificial Intelligence), robotics, and automation, Industry 4.0 infrastructures allow machines, devices, and systems to communicate seamlessly, gather and analyze data in real time, and make autonomous decisions (Nguyen et al., 2022). This interconnectedness leads to optimized production, reduced resource consumption, and greater agility in response to volatile market demands and supply chain disruptions, ultimately making manufacturing operations more resilient.
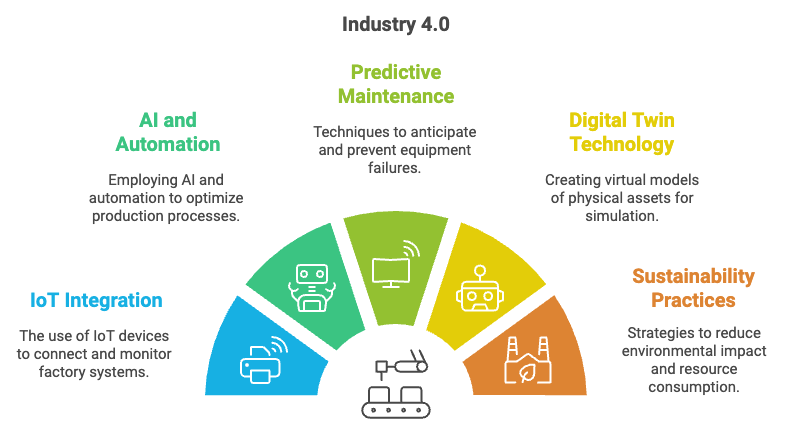
Figure 1: Industry 4.0 impacts on manufacturing and smart factories.
Emerging studies further highlight Industry 4.0’s potential to bolster global competitiveness by enabling cost-effective, customized production and accelerating time to market. According to PwC (2022), firms that have adopted digital manufacturing tools report both immediate productivity gains and heightened flexibility when coping with unexpected events, such as sudden shifts in raw material availability or consumer demand. Meanwhile, the high-speed connectivity provided by 5G networks is increasingly recognized as a core enabler of real-time data exchange and automation, particularly in complex manufacturing environments where milliseconds can determine throughput and quality outcomes (Li et al., 2023).
At the heart of Industry 4.0 is the concept of the smart factory, a digitally enhanced environment where production systems are connected through a central data network—often via IoT sensors and cloud computing. Each piece of equipment is embedded with sensors collecting data on performance, environmental conditions, and product quality, data then analyzed by AI algorithms to inform decision-making (Zhang and Chen, 2021). These systems facilitate a shift from reactive or scheduled maintenance models to predictive, data-driven approaches, thereby reducing unscheduled downtime and minimizing resource use. In line with KPMG’s (2023) findings, such connected environments also support remote monitoring, allowing manufacturers to manage operations across multiple sites and optimize production flows in real time. For emerging economies, this transition offers a leapfrogging opportunity: instead of inheriting legacy infrastructures, they can implement advanced technologies that align with global best practices from the onset.
Numerous studies emphasize that establishing a successful smart factory requires interdisciplinary knowledge, combining operational expertise with data science and systems engineering (Mittal et al., 2022). Manufacturers must invest in workforce upskilling, cybersecurity measures, and strategic technology roadmaps to realize the full benefits of Industry 4.0. This alignment of human capital and digital solutions is not only critical for day-to-day efficiency but also for fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. According to EY (2024), organizations that prioritize training programs and cross-functional collaboration significantly outperform competitors in terms of operational agility and financial performance.
Leading manufacturers such as Siemens and Bosch illustrate how large-scale Industry 4.0 adoption can transform conventional facilities into models of automation, connectivity, and resilience. Siemens’ Amberg Electronics Plant has reported that over 75% of its production processes are both automated and connected, leveraging IoT sensors and AI algorithms for real-time performance monitoring (Kamble, Gunasekaran, and Dhone, 2020). Digital twin technology underpins this approach: virtual replicas of machines provide continuous insights into production conditions, enabling predictive diagnostics that schedule maintenance at optimal intervals. This data-driven maintenance strategy substantially reduces downtime and associated costs while boosting overall equipment effectiveness.
Bosch has likewise championed Industry 4.0 through its Connected Industry initiative, embracing AI-driven analytics, robotics, and automated decision-making. By analyzing production data with machine learning algorithms, Bosch accurately forecasts demand and adjusts scheduling to balance efficiency with market needs (Mittal et al., 2022). The company’s integration of digital twins further allows operators to simulate production modifications before implementing them, minimizing risks and improving resource allocation. Through these technologies, Bosch not only maintains product quality and responsiveness but also paves the way for scalable, intelligent manufacturing processes that can adapt to evolving consumer preferences.
A crucial aspect of smart manufacturing is predictive maintenance, which relies on sensor data to evaluate machine health and avert mechanical failures before they occur. By analyzing factors such as vibration, temperature, and energy consumption, predictive algorithms can detect abnormal patterns that signify potential malfunctions (Nguyen et al., 2022). According to Deloitte (2021), manufacturers that transition from reactive to predictive maintenance models report a 20–30% decrease in maintenance costs and a comparable reduction in unplanned downtime. Predictive maintenance not only prolongs machine lifecycles but also improves overall safety, as machinery operating outside specified conditions is flagged immediately for inspection or repair.
Digital twin technology further strengthens this proactive approach, creating a virtual representation of an asset or entire production line that updates in real time. By feeding data from IoT sensors into digital twins, manufacturers can simulate various operating conditions, identify inefficiencies, and test process changes in a low-risk virtual setting (Zhang and Chen, 2021). As a result, resources can be allocated more strategically, and production workflows can be fine-tuned without causing disruptions on the factory floor.
The widespread adoption of 5G networks is another vital driver of Industry 4.0, enabling high-speed, low-latency communication necessary for real-time machine-to-machine interactions. Industry reports suggest that 5G can reduce latency by up to 90% compared to previous network standards, a shift that is essential for tasks like remote robotic control and automated guided vehicles in warehouses (Li et al., 2023). In many emerging economies, where building extensive wired infrastructure can be cost-prohibitive, 5G offers an effective path to modernizing manufacturing operations (PwC, 2022). This next-generation connectivity empowers local factories to run complex analytics, leverage AI-driven systems, and react swiftly to production changes, aligning them with global counterparts and enhancing export competitiveness.
AI and machine learning have become central to smart manufacturing strategies, offering advanced capabilities for optimizing production lines, reducing energy consumption, and enhancing quality control. In an AI-enabled environment, machine learning models can predict fluctuations in consumer demand, fine-tune production parameters, and instantly detect anomalies that may compromise quality (Frank et al., 2021). Advanced analytics also facilitate predictive quality management, catching defects at the earliest stages. A study by KPMG (2023) confirms that intelligent automation not only cuts operational costs but also significantly shortens lead times, allowing companies to respond rapidly to evolving market conditions.
Collaborative robots (cobots) exemplify how robotics and AI can reshape labor dynamics within smart factories. Equipped with sensors and real-time data processing capabilities, cobots work safely alongside human operators and can be reprogrammed easily to adapt to changing product specifications. This synergy boosts throughput and allows human workers to concentrate on tasks requiring creativity and problem-solving (Mittal et al., 2022). In emerging markets, cobots offer the dual benefits of retaining cost-effectiveness while improving manufacturing precision and repeatability.
Industry 4.0 also promotes environmental stewardship by enabling precision resource management. IoT-based monitoring systems track energy consumption, water usage, and emissions across the production cycle, and AI algorithms identify areas for efficiency gains (Nguyen et al., 2022). Manufacturers can utilize these insights to reduce waste, shrink carbon footprints, and limit the environmental impact of industrial operations. According to EY (2024), companies adopting Industry 4.0 technologies in pursuit of sustainable manufacturing goals often see concurrent cost savings—particularly when they leverage real-time data to optimize energy utilization and align production more closely with demand.
The transition to Industry 4.0 and the rise of smart factories are reshaping global manufacturing, driving productivity, and enhancing flexibility in an increasingly unpredictable market. By leveraging technologies such as AI, digital twins, 5G connectivity, and collaborative robotics, manufacturers can build resilient, data-driven systems able to anticipate disruptions, reduce operational inefficiencies, and adapt swiftly to demand fluctuations (PwC, 2022). Moreover, these technologies contribute to broader sustainability objectives, guiding companies toward a future where operational excellence and environmental responsibility reinforce one another. As Industry 4.0 continues to evolve, supported by interdisciplinary research and strategic corporate investments, it will likely define the next generation of manufacturing paradigms—offering a pathway to smarter, more connected, and more sustainable industrial operations.
6.2. Smart Supply Chains in Healthcare
The healthcare industry relies on efficient supply chain operations to ensure the continuous availability of critical medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines. Unlike consumer goods, healthcare products have direct implications for patient well-being, making reliable demand forecasting and inventory management a central priority (Zhang and Shaw, 2021). Moreover, these supply chains must adhere to stringent quality and safety requirements to safeguard patient outcomes—necessitating robust processes for storage, handling, and distribution (KPMG, 2024). Because of the rapidly changing landscape of global healthcare, organizations are increasingly turning to digital technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain to streamline operations and mitigate risk (Shah et al., 2023). These transformations promise to enhance both day-to-day efficiency and long-term resilience in healthcare supply chains, particularly when facing shocks like pandemics and natural disasters (Deloitte, 2022).
Recent analyses underline the importance of continuous improvement in healthcare supply chain structures, especially in areas characterized by high levels of complexity and strict regulatory oversight (PwC, 2023). Indeed, healthcare supply chains differ significantly from their counterparts in consumer goods or automotive sectors due to the urgent, life-saving nature of the products they deliver. A shortage of critical medical devices or essential medicines can immediately affect patient treatment, underscoring the pivotal role of supply chain transparency and agility (Modgil et al., 2021). This emphasis on availability goes hand in hand with the need to maintain product integrity and regulatory compliance. Medical products often require temperature-controlled storage and highly specialized handling, while facilities must rigorously track each unit of inventory for quality assurance and legal reporting (EY, 2025).
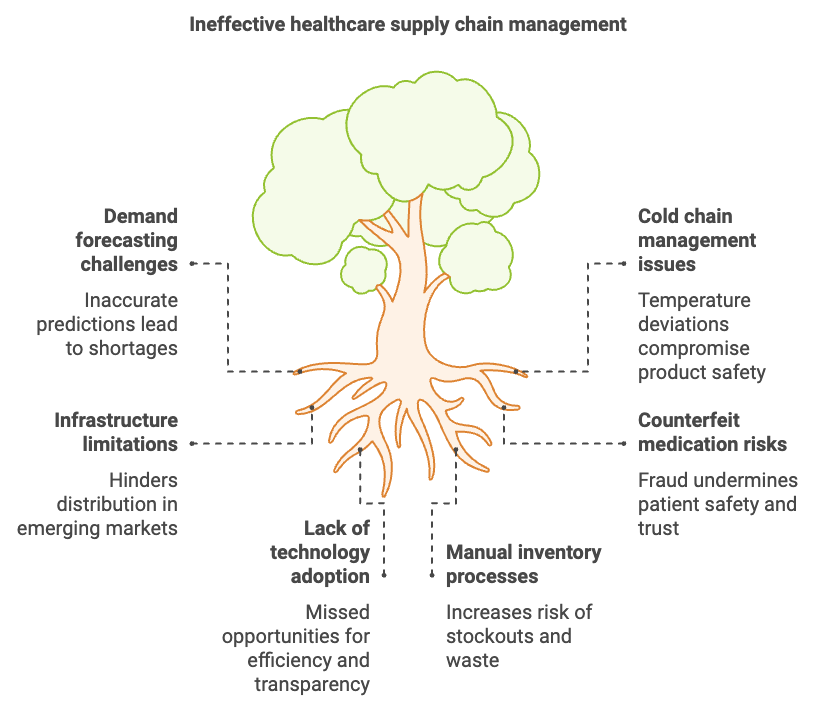
Figure 2: Ineffective complexities of supply chain management in Healthcare industry.
One of the most complex areas in healthcare logistics is cold chain management, the specialized process of transporting and storing temperature-sensitive items such as vaccines, biologics, and certain medications (Narang and Singh, 2022). Small deviations in temperature or humidity can compromise a product’s effectiveness, creating significant financial and patient safety risks. Consequently, healthcare organizations invest heavily in cold chain systems designed for climate-controlled storage and real-time monitoring. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the distribution of vaccines with highly specific temperature requirements illuminated both the critical importance of robust cold chain solutions and the operational challenges of scaling these systems on a global level (Deloitte, 2022).
To maintain the integrity of products, cold chain management often integrates IoT-driven sensors that track environmental conditions and transmit alerts when parameters deviate from acceptable ranges (Shah et al., 2023). For example, UPS Healthcare implemented an IoT-enabled platform to monitor vaccine shipments continuously, enabling timely interventions in the event of equipment failures or unforeseen logistical disruptions (EY, 2025). This approach is especially vital in emerging markets, where infrastructure limitations and long transit times can heighten the risk of temperature excursions.
From an academic standpoint, the optimization of healthcare supply chains brings together insights from logistics, public health, operations research, and information technology (Modgil et al., 2021). Robust demand forecasting, coupled with real-time data analysis, can significantly reduce waste from expired medications and minimize stockouts—both of which have direct ramifications for patient care (Zhang and Shaw, 2021). Predictive analytics models using machine learning can account for multifaceted variables such as epidemiological data, demographic trends, and prescription patterns to forecast spikes in demand more accurately (Sheikh et al., 2023). These methods are particularly beneficial in emerging economies, where healthcare needs may vary widely across different regions, making precise resource allocation critical to improving equity in access to medical supplies (PwC, 2023).
Blockchain technology has also gained traction as a means of ensuring transparency and security throughout the healthcare supply chain. By creating an immutable ledger for each transaction and movement of goods, blockchain enables stakeholders to trace products back to their origin, verify authenticity, and confirm regulatory compliance (KPMG, 2024). This functionality is especially valuable in preventing the proliferation of counterfeit medications, a persistent issue in low- and middle-income countries. Additionally, during large-scale immunization campaigns, such as the global rollout of COVID-19 vaccines, blockchain can confirm that each batch remains within required storage parameters and that distribution aligns with official protocols (Narang and Singh, 2022).
Leading pharmaceutical firms like Pfizer and Moderna have showcased how AI-driven inventory management and demand forecasting can be deployed effectively on a large scale. In rolling out COVID-19 vaccines, both companies employed data analytics platforms that incorporated real-time data, historical sales figures, and international regulatory guidelines to distribute stock efficiently (Sheikh et al., 2023). This proactive approach minimized shortages even amid significant fluctuations in demand, thereby expediting vaccine administration in multiple regions. The success of these data-centric strategies underscores the potential for broader application of AI in healthcare logistics, particularly when paired with advanced connectivity solutions such as 5G for real-time data transmission and cloud-based collaboration (Zhang and Shaw, 2021).
Major logistics providers have also played a pivotal role in elevating cold chain reliability. UPS Healthcare, for instance, deployed IoT-enabled containers and temperature sensors to maintain optimal conditions during transit and trigger immediate notifications if deviations occurred (EY, 2025). Likewise, FedEx and DHL ramped up their investment in specialized cold storage facilities and advanced tracking systems, reflecting a broader trend toward end-to-end digitalization in healthcare distribution networks (Deloitte, 2022). In both developed and emerging economies, these innovations help address longstanding logistical bottlenecks, supporting more precise tracking of shipments and faster incident response.
In regions with limited healthcare infrastructure, technology-driven supply chain optimization holds particular promise. AI-based demand forecasting can direct scarce resources more effectively, ensuring that rural clinics are not overshadowed by larger urban hospitals (PwC, 2023). Meanwhile, blockchain offers a robust mechanism for confirming drug authenticity in areas where counterfeit products remain a significant threat (Narang and Singh, 2022). By adopting these tools, emerging economies can mitigate some of the systemic issues that hinder effective healthcare delivery, enabling more consistent access to vital treatments and medications (KPMG, 2024). Furthermore, the incorporation of IoT sensors can help overcome infrastructure constraints by providing constant visibility into product location and condition, even when last-mile delivery is complicated by rough terrain or inadequate transportation networks (Shah et al., 2023).
Smart supply chain management in the healthcare sector is no longer an optional upgrade but an essential strategic imperative. The global experience of COVID-19 underscored the ramifications of supply chain failures, including waste of high-value medical products and life-threatening delays in patient care (Deloitte, 2022). By leveraging digital tools such as AI, IoT, and blockchain, healthcare organizations can enhance demand forecasting, maintain stringent cold chain conditions, and verify product authenticity at every step of the journey from manufacturer to patient (Zhang and Shaw, 2021). These innovations collectively contribute to a more transparent, efficient, and resilient supply chain ecosystem—one capable of adapting to public health crises, regional disparities in infrastructure, and evolving regulatory standards (KPMG, 2024). Ultimately, the widespread adoption of these technologies promises to bolster patient safety, reduce costs, and improve health outcomes on a global scale.
6.3. Smart Supply Chains in Retail
Omnichannel supply chain strategies are increasingly vital in the retail sector, reflecting a shift in consumer expectations toward seamless, flexible, and rapid purchasing options across both physical and digital channels. In contrast to conventional retail models that isolate online and offline operations, omnichannel strategies unify these dimensions to provide a consistent customer experience (Chen and Park, 2022). By integrating retail stores, warehouses, and direct-to-consumer networks, omnichannel supply chains allow businesses to dynamically allocate inventory and fulfill orders from the location best positioned to serve the customer, be it a local store or a centralized distribution center (PwC, 2025). Consequently, retailers can offer convenient services such as “buy online, pick up in store” (BOPIS), same-day delivery, and real-time product availability—all of which contribute to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty (Deloitte, 2023).
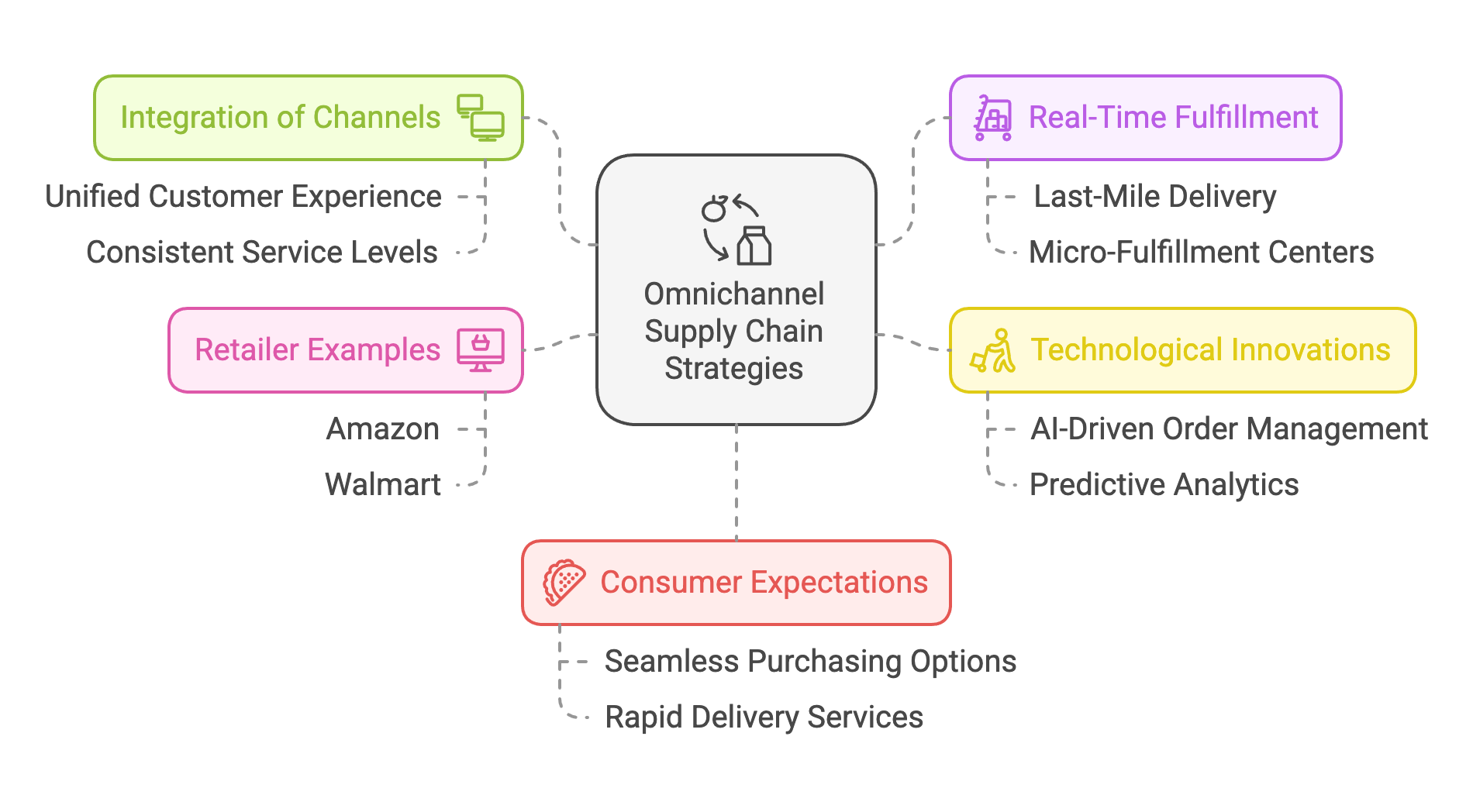
Figure 3: Smart supply chain in retail - Scopes of omnichannel strategy.
A crucial component of omnichannel supply chains is the capacity for real-time fulfillment and last-mile delivery, both of which have become increasingly complex and costly. Recent analyses suggest that last-mile delivery can account for as much as 53% of total shipping costs, driven by changing consumer demands for speed and convenience (KPMG, 2022). To meet these expectations, retailers are experimenting with micro-fulfillment centers in urban areas, leveraging automation and data analytics to keep popular items close to end consumers (Rodriguez, Freedman, and Nguyen, 2022). These smaller, strategically located facilities enable faster delivery and reduced transportation expenses, an approach especially useful in densely populated regions where traffic congestion can prolong conventional warehouse-to-door transit times. In emerging markets, micro-fulfillment can also mitigate infrastructural challenges by decentralizing inventory storage and reducing dependence on large, centralized distribution hubs (EY, 2024).
From an academic perspective, omnichannel supply chain management sits at the intersection of logistics, consumer behavior, and digital transformation, drawing heavily on predictive analytics, machine learning, and real-time data exchange (Smith, Li, and Thompson, 2023). The ability to collect and interpret high-volume, high-velocity data enables more accurate forecasting of product demand, improving both inventory turnover and fill rates (Chen and Park, 2022). These capabilities not only reduce the risk of stockouts or surplus but also allow retailers to adapt quickly to demand fluctuations triggered by seasonality, promotions, or external factors such as local events and weather patterns. In emerging economies, the integration of online marketplaces with last-mile solutions offers smaller retailers the opportunity to reach broader customer bases, leveling the playing field against more established global brands (PwC, 2025).
Leading retailers exemplify the practical advantages of omnichannel transformation. Amazon’s ecosystem integrates extensive distribution networks with advanced demand forecasting, machine learning algorithms, and automated robotics, enabling rapid, reliable shipping under programs like Prime (Rodriguez, Freedman, and Nguyen, 2022). Meanwhile, Walmart leverages its widespread physical footprint by designating local stores as fulfillment nodes—an approach that shortens delivery routes and empowers customers to pick up online orders in-store (KPMG, 2022). By capitalizing on these assets, Walmart can compete effectively with pure online players, offering flexibility and speed to customers who value multiple buying and delivery options (Deloitte, 2023). The success of both firms underscores the importance of robust logistics infrastructure, data analytics, and process automation in building a truly omnichannel supply chain.
Beyond distribution and fulfillment, robotics and AI-driven order management systems serve as cornerstones of modern omnichannel networks. Automated picking and sorting processes reduce labor costs and accelerate throughput in fulfillment centers (Smith, Li, and Thompson, 2023). Intelligent order management systems analyze data streams from inventory levels, point-of-sale transactions, and external indicators such as online shopping trends to optimize how and where orders are processed (Chen and Park, 2022). This level of operational agility helps retailers to avoid bottlenecks during peak periods and to adapt quickly to emerging consumer trends, thereby improving overall service quality. For example, real-time analytics can identify imminent stock shortages in particular regions, automatically triggering replenishment from the nearest distribution center or store.
In emerging markets, these innovations have opened up new opportunities for retailers faced with infrastructural and logistical constraints. The combination of local micro-fulfillment, AI-based inventory tracking, and last-mile delivery networks—often supported by smaller third-party logistics providers—allows businesses to offer competitive lead times despite limited transportation infrastructure (EY, 2024). Additionally, IoT sensors and GPS trackers help monitor shipments in real time, providing visibility that mitigates the risk of damage or theft en route. This enhanced transparency fosters greater consumer trust, especially in markets where delays and product authenticity concerns may have traditionally deterred online shopping (PwC, 2025).
As consumer expectations continue to rise, retailers must evolve their supply chains to be not only faster and more flexible but also more resilient to disruptions. Research indicates that omnichannel operations supported by digital tools can reduce total supply chain costs by up to 15% while increasing service levels by 25% (KPMG, 2022). Meanwhile, these networks also enable better risk management, as inventory can be rerouted from one channel to another in response to unforeseen events such as natural disasters, labor strikes, or demand surges (Deloitte, 2023). Ultimately, the development of an omnichannel strategy represents a transformative step for retailers seeking to remain competitive in an environment shaped by immediacy, convenience, and technological innovation. By embracing micro-fulfillment centers, AI-driven order management, and integrated data analytics, retailers can deliver a unified customer experience across channels, turning logistics excellence into a key differentiator in a rapidly changing market.
6.4. Smart Supply Chains in Logistics and Distribution
In an era of heightened globalization, managing logistics and distribution within supply chains has become an intricate endeavor. Modern supply chains traverse multiple geographical regions, rely on diverse transportation modes, and must coordinate warehousing, inventory management, and delivery schedules with precision (KPMG, 2023). Simultaneously, external disruptions such as shifting consumer demand, geopolitical tensions, and environmental factors—including severe weather events—compound the complexity (Deloitte, 2021). As companies expand their operations worldwide, they face the dual imperatives of reducing costs and improving speed while maintaining operational flexibility to adapt to unforeseen circumstances (PwC, 2024).
A central tenet of this evolution is the growing reliance on AI-driven logistics systems, which leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize transportation routes, shorten delivery times, and modernize warehouse processes (Gao et al., 2023). By processing vast datasets—encompassing historical shipment information, real-time vehicle location, and macro-level inputs such as fuel prices—logistics providers can anticipate disruptions and forecast demand more accurately (Huang and Chang, 2022). These predictive capabilities enable a shift from reactive to proactive management, particularly in emerging markets with variable infrastructure. There, AI-based approaches help local players compete by automating routine tasks, rationalizing resource allocation, and providing deeper visibility into supply chain operations (EY, 2025).
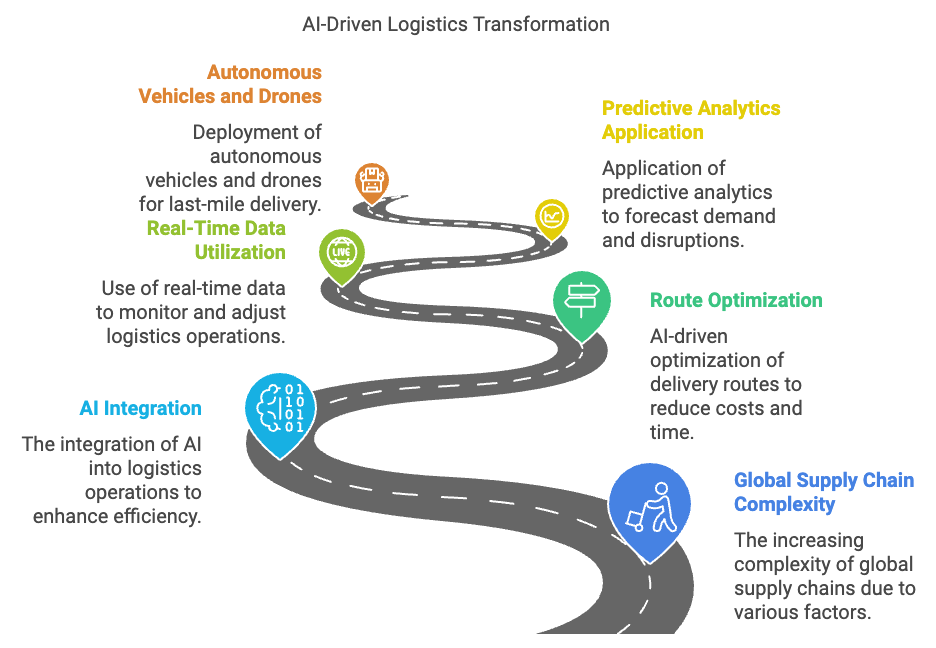
Figure 4: AI-driven logistics transformation as key part of smart supply chain.
Leading logistics firms like DHL and UPS offer tangible examples of how AI can streamline distribution networks. DHL integrates real-time analytics and predictive modeling to analyze traffic patterns, vehicle positioning, and package volume across its global fleet (KPMG, 2023). This allows for dynamic route adjustments that reduce unnecessary mileage, lower fuel consumption, and mitigate environmental impacts. Moreover, advanced forecasting algorithms help DHL anticipate spikes in demand, ensuring sufficient capacity without overburdening its resources (Huang and Chang, 2022).
UPS employs a similar methodology through its ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation) system, which utilizes machine learning to determine optimal delivery routes, accounting for variables such as stop sequence, road closures, and weather (Deloitte, 2021). By minimizing miles driven, UPS lowers fuel expenses and shortens delivery cycles. Additionally, real-time analytics facilitate swift adjustments if unexpected disruptions—such as severe storms or traffic jams—emerge. Collectively, these AI-driven practices empower logistics providers to handle complex, global operations with heightened efficiency and reliability.
In the realm of warehousing, AI-powered systems manage inventory levels, monitor storage conditions, and optimize space utilization (Ren et al., 2021). By analyzing data from sensors and warehouse management platforms, these algorithms can predict demand fluctuations and reorder inventory accordingly, thus preventing both overstocking and stockouts (Gao et al., 2023). For instance, if data projections indicate a surge in e-commerce orders for seasonal goods, the AI system can preemptively allocate warehouse slots, ensuring that items are readily accessible for picking and packing.
Real-time analytics act as a linchpin for managing disruptions, allowing providers to detect potential bottlenecks as they occur (PwC, 2024). If traffic congestion disrupts a major route, AI-driven software can promptly suggest alternative paths, reducing transit delays. This responsiveness is particularly valuable in emerging regions where infrastructure challenges—such as limited road networks or inconsistent public utilities—amplify logistical uncertainty (EY, 2025). With real-time visibility into goods movement, logistics companies can more accurately commit to delivery times, ultimately strengthening customer satisfaction and trust.
One of the most transformative frontiers in logistics is the adoption of autonomous vehicles and drones for last-mile delivery (Hwang et al., 2022). Traditionally, the final stretch of the supply chain constitutes the costliest and most time-intensive phase, especially in high-density urban centers or remote locales. By employing autonomous vans or robotic carriers, logistics operators can diminish their reliance on human drivers and mitigate labor costs (Deloitte, 2021). Drones, meanwhile, present a promising solution for delivering light parcels—such as critical medications or urgent documents—directly to customers who may be situated in hard-to-reach areas.
Amazon’s Prime Air initiative demonstrates the potential of drone technology to expedite deliveries and enhance customer satisfaction (Ren et al., 2021). However, widespread deployment remains constrained by regulatory limitations and technological hurdles, including safety protocols and air traffic management (KPMG, 2023). Nonetheless, ongoing pilot programs underscore the significant efficiency gains that autonomous vehicles and drones could bring to last-mile logistics once these obstacles are addressed.
Predictive analytics have emerged as a strategic asset in smart logistics, enabling providers to align operational decisions with anticipated demand cycles. By incorporating data such as seasonal trends, macroeconomic indicators, and historical buying patterns, AI tools can forecast spikes in consumer purchases and guide resource allocation accordingly (Hwang et al., 2022). These insights prove particularly vital for sectors with strong seasonal variability—like retail or agriculture—and can be crucial in emerging markets where supply chain bottlenecks are intensified by limited resources (PwC, 2024).
Additionally, sustainability concerns are reshaping the logistics landscape, compelling companies to optimize routes, reduce emissions, and minimize wasteful practices (EY, 2025). AI can recommend more eco-friendly packaging, schedule deliveries to avoid peak congestion, and suggest modes of transport with lower carbon footprints (Huang and Chang, 2022). While such measures align with corporate social responsibility goals, they also yield tangible cost savings through reduced fuel usage and fewer idle miles. The emphasis on sustainable logistics is particularly pertinent in areas lacking robust recycling infrastructure, making it even more essential to curtail excessive material use and energy consumption.
AI-driven approaches in logistics and distribution mark a pivotal shift from reactive to proactive supply chain management. By harnessing massive data streams—spanning traffic conditions, warehouse metrics, and environmental factors—logistics providers can refine route optimization, enhance inventory accuracy, and build greater resilience against disruptions (Gao et al., 2023). The practical successes of firms like DHL and UPS illuminate how real-time analytics and predictive modeling translate into cost savings, improved delivery times, and reduced environmental impact (Deloitte, 2021). Looking ahead, emerging technologies such as autonomous vehicles, drones, and advanced predictive models hold the potential to further revolutionize last-mile delivery, enabling faster and more efficient service. By embracing AI, companies not only elevate their operational excellence but also craft supply chains that are sustainable, adaptable, and well-positioned for the continually shifting dynamics of global commerce (PwC, 2024).
6.5. Smart Supply Chains in Energy and Utilities
The energy and utilities sector provides the foundational resources—electricity, water, and natural gas—that power industries and households across the globe. In an era of rising global demand and heightened environmental awareness, smart supply chain strategies have become indispensable for ensuring reliable, efficient, and sustainable resource management (KPMG, 2023). The adoption of digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, and blockchain-based systems enables utility providers to optimize resource allocation, minimize losses, and balance supply with ever-fluctuating demand (Deloitte, 2021). These innovations not only improve operational efficiency but also contribute to broader goals such as reducing carbon footprints and enhancing energy equity in developing regions (Zhao, Wang, and Zhao, 2022).
Figure 5: Optimization in energy supply chain.
A key innovation propelling change in this sector is the smart grid, which augments traditional energy infrastructure with digital monitoring and real-time data analytics. Smart grids rely on IoT sensors, communication networks, and automated controls to detect outages, balance electricity loads, and integrate renewable sources (PwC, 2024). For instance, IoT-enabled devices can pinpoint voltage inconsistencies, track surges in consumption, and autonomously reroute power to prevent network overloads (Kim and Park, 2023). By enhancing situational awareness, smart grids reduce energy loss, optimize maintenance schedules, and adapt to emerging challenges such as extreme weather events. Similar IoT-enabled mechanisms have also been applied to water and natural gas networks, where continuous monitoring of pressure levels and flow rates allows utilities to detect leaks and improve overall distribution efficiency (Zhao, Wang, and Zhao, 2022).
From an academic standpoint, research on smart supply chains in energy intersects with fields such as environmental engineering, systems management, and data science (Kim and Park, 2023). Comprehensive adoption of IoT devices demands secure, high-bandwidth connectivity and sophisticated analytics capable of converting raw data into actionable insights. In emerging markets, these tools offer the means to leapfrog older infrastructure, thereby reducing energy losses and broadening access. Furthermore, decentralized IoT monitoring empowers local communities to track their consumption patterns and implement resource-saving measures, fostering a culture of sustainable usage (EY, 2025).
Global energy players like General Electric (GE) and Siemens have played pivotal roles in mainstreaming smart grid solutions and demonstrating their tangible benefits. GE has merged IoT and analytics across multiple power networks, enabling utilities to make data-driven decisions ranging from fault detection to real-time power rerouting (Li, Chen, and Ko, 2025). This heightened visibility improves grid stability, lowers operational costs, and curbs carbon emissions by minimizing wasteful generation. Meanwhile, Siemens focuses on integrating renewable energy sources—such as solar and wind—into existing grids, a process complicated by the intermittent nature of renewables (Zhao, Wang, and Zhao, 2022). By leveraging machine learning algorithms, Siemens’ digital grids proactively balance the flow between green and conventional power, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels during peak times and improving overall grid resilience (PwC, 2024).
Predictive analytics have emerged as a cornerstone in managing energy demand, leveraging historical consumption data, weather patterns, and economic indicators to gauge future needs (Kim and Park, 2023). Utilities employ these models to anticipate seasonal or event-based surges, enabling them to adjust production schedules or secure additional energy resources proactively. Accurate forecasts help providers avert shortages, mitigate costly emergency purchases, and align with sustainability objectives by reducing reliance on high-emission “peaking” plants (Deloitte, 2021). Moreover, automated demand-response programs—guided by AI—can curtail consumption in non-critical areas or incentivize users to shift their usage during peak periods, relieving stress on the grid and lowering operational expenses (KPMG, 2023).
In emerging markets where supply chain bottlenecks are more common, predictive tools are especially valuable for optimizing limited infrastructure (EY, 2025). Through real-time analytics, utilities can target resource allocation to the areas most in need, expanding energy access in a controlled yet efficient manner. This data-centric approach also supports broader goals like rural electrification, as utilities can identify underserved regions and forecast the return on investment for grid expansions or off-grid solutions (Li, Chen, and Ko, 2025).
Blockchain technology has gained traction in the energy sector for its capacity to record and verify transactions securely, facilitating transparent energy trading (Zhao, Wang, and Zhao, 2022). In decentralized grids where individual consumers generate their own power—often through solar panels—blockchain ensures that each kilowatt-hour produced and sold is accurately tracked in an immutable ledger (Li, Chen, and Ko, 2025). This real-time verification not only discourages fraudulent transactions but also eliminates the need for costly intermediaries, thereby lowering transaction fees. Moreover, blockchain-based platforms can validate renewable energy credits (RECs), guaranteeing that claims about green power usage are substantiated (KPMG, 2023).
For regions plagued by inconsistent electricity access, the decentralized nature of blockchain can expedite infrastructure development. By allowing local generation and direct peer-to-peer trading, communities can bypass traditional centralized grids (Deloitte, 2021). This decentralized approach not only enhances system resilience—spreading the risk of outages across a larger, more diverse network—but also encourages investment in clean energy projects, which can flourish without reliance on top-down utility models (EY, 2025).
The integration of AI, IoT, and blockchain within energy and utilities is reshaping how essential resources are produced, monitored, and distributed. Through smart grid systems, advanced predictive analytics, and decentralized trading models, utilities can enhance reliability, reduce operational costs, and accelerate the global transition toward renewable energy sources (PwC, 2024). Leaders such as GE and Siemens underscore the feasibility of these digital transformations, while emerging economies benefit from opportunities to modernize infrastructure without incurring the inefficiencies of legacy systems. As sustainability pressures intensify and demand surges, smart supply chains in the energy sector will remain central to achieving a resilient, eco-friendly, and accessible global energy network (KPMG, 2023).
6.6. Conclusion and Further Learning
In conclusion, industry-specific innovations are revolutionizing supply chain management, enabling businesses to optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability across various sectors. By embracing technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain, companies can build more resilient and responsive supply chains that meet the demands of modern consumers while mitigating risks. These advancements are not just transforming industries individually, but collectively pushing the boundaries of what supply chains can achieve in terms of efficiency, transparency, and flexibility.
Exploring the following prompts will open new doors of understanding into how industry-specific innovations are transforming supply chains in every sector. By engaging deeply with these topics, you will gain valuable insights into the practical applications of AI, IoT, blockchain, and other cutting-edge technologies that are driving the future of supply chain management.
How does Industry 4.0 fundamentally redefine traditional manufacturing practices by integrating advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, robotics, and cyber-physical systems, and what are the transformative benefits of implementing smart factories, particularly in terms of productivity, efficiency, data-driven decision-making, and operational agility?
What role do predictive maintenance systems and digital twins play in minimizing machine downtime and enhancing overall production efficiency in smart factories, and how can AI-driven predictive analytics and real-time monitoring be used to optimize equipment performance, reduce maintenance costs, and extend machinery lifecycles?
How can AI and IoT technologies revolutionize cold chain management in healthcare by providing real-time monitoring of temperature-sensitive products, ensuring compliance with safety standards, and enabling predictive insights for inventory management, transportation, and storage of critical medical supplies like vaccines and biologics?
What are the most effective strategies for implementing AI-driven inventory management in healthcare supply chains, particularly for optimizing stock levels, reducing waste, preventing stockouts, and ensuring the timely availability of life-saving products, while meeting regulatory and safety standards?
How does blockchain technology improve transparency, security, and traceability in pharmaceutical supply chains, particularly in cold chain logistics, by providing a decentralized and immutable record of product handling, and how does it help mitigate counterfeit drugs and ensure regulatory compliance?
What are the key challenges in implementing omnichannel supply chain strategies in retail, such as managing complex logistics, inventory synchronization, and real-time order fulfillment across multiple sales channels, and how can AI-driven solutions optimize these processes for improved customer satisfaction and operational efficiency?
How can micro-fulfillment centers, powered by robotics and AI, help retailers meet the increasing consumer demand for faster, more flexible delivery options, and what are the key benefits of strategically positioning inventory closer to consumers to reduce delivery times and optimize last-mile logistics?
What role do AI-powered order management systems play in predicting consumer demand, optimizing inventory across multiple sales channels, and managing real-time order fulfillment, and how do these systems help retailers minimize stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and enhance customer satisfaction?
How does AI-driven logistics, including machine learning and real-time data analytics, transform route optimization, fleet management, and warehouse operations, and what impact does this have on reducing transportation costs, improving delivery speed, and enhancing overall logistics efficiency?
How can real-time data analytics and AI-driven algorithms be used to effectively respond to supply chain disruptions in logistics caused by external factors like weather, traffic, and geopolitical events, and what predictive strategies can companies adopt to mitigate risks and ensure continuity of operations?
What are the key advantages of using autonomous vehicles and drones for last-mile delivery in logistics, and how do these innovations enhance operational efficiency, reduce fuel and labor costs, and improve the speed and accuracy of delivery, especially in urban environments with high demand for faster fulfillment?
How do smart grids and IoT technologies improve resource management in the energy and utilities sector by enabling real-time monitoring, demand forecasting, and data-driven optimization of energy distribution networks, and what impact does this have on reducing energy waste and improving grid stability?
What role does predictive analytics play in forecasting energy demand in the utilities sector, and how does the accurate prediction of consumption patterns enhance the efficiency of energy supply networks, particularly in balancing load distribution, reducing peak demand, and optimizing resource allocation?
How does blockchain technology enhance transparency, security, and trust in decentralized energy supply networks, and what are its specific applications in tracking energy generation, consumption, and transactions in smart grid systems, particularly in peer-to-peer energy trading and renewable energy certification?
How can AI-driven energy management systems optimize resource usage and reduce consumption during peak demand periods in the energy and utilities sector, and what role do machine learning algorithms play in predicting demand fluctuations and automating the efficient allocation of resources?
What are the key innovations in smart logistics, such as AI-driven optimization platforms, autonomous vehicles, and real-time data analytics, that allow logistics providers to manage the growing complexity of global supply chains, and how do these technologies improve scalability, accuracy, and sustainability in logistics operations?
How can AI and machine learning be applied to predict demand fluctuations in logistics and supply chains, and what real-time data sources and algorithms are most effective in enabling companies to adjust logistics strategies dynamically to prevent disruptions, overstocking, or understocking?
How does predictive analytics enable manufacturing companies to optimize production schedules, reduce material waste, improve resource allocation, and enhance overall production efficiency, and what role do AI-driven models play in forecasting demand, managing inventory, and preventing production bottlenecks?
What lessons can be learned from companies that have successfully integrated smart factory technologies, such as AI, IoT, and robotics, into their supply chains, and how can these best practices be scaled across different industries to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance competitiveness?
How can blockchain, AI, and IoT technologies collectively transform the future of smart supply chains across diverse industries, ensuring greater sustainability, transparency, and resilience, and what are the specific use cases where the integration of these technologies leads to significant improvements in operational efficiency and risk management?
Let these questions challenge your thinking, inspire curiosity, and motivate you to explore how smart supply chains can create value, improve efficiency, and enhance sustainability in a rapidly changing world. As you dive into these prompts, you’ll be equipped to lead the way in applying these innovations to your own industry.
Comments