Chapter 10
Implementing and Scaling Smart Supply Chains
"Digital transformation isn’t just about adopting new technologies—it’s about rethinking how we operate, collaborate, and scale to meet the demands of an ever-evolving global marketplace." — Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft.
Chapter 10, Implementing and Scaling Smart Supply Chains, provides a comprehensive guide to transforming traditional supply chains into smart, digitally-powered ecosystems. It begins with assessing a company’s digital maturity and readiness for technological adoption, followed by creating a step-by-step roadmap for digital transformation. The chapter emphasizes the importance of leveraging partnerships and ecosystems for successful implementation, outlines key metrics and KPIs to measure success, and highlights best practices for scaling and sustaining supply chain innovations over time. By integrating cutting-edge technologies such as AI, blockchain, and cloud platforms, businesses can achieve long-term competitiveness and operational efficiency.
10.1. Digital Maturity and Technological Adoption
Digital maturity has emerged as a critical determinant of an organization’s ability to successfully implement advanced supply chain technologies. It encompasses not just the adoption of new tools and systems but also the alignment of an organization’s culture, workforce skill sets, and strategic objectives with digital transformation initiatives (KPMG, 2023; PwC, 2024). Within the realm of supply chains, digital maturity shapes how effectively a company can integrate AI, IoT, blockchain, and digital twin solutions to enable real-time decision-making, heightened visibility, and agile responses to market disruptions (Deloitte, 2023). As supply chains grow more interconnected and reliant on data-driven processes, assessing and enhancing digital maturity becomes a foundational step toward creating resilient, future-ready operations.
The notion of digital maturity refers to the degree to which an organization has embedded digital technologies across its workforce, infrastructure, and strategic framework (Chong and Lu, 2022). For supply chain management, this maturity translates into the capability to leverage advanced analytics, machine learning, and automation to optimize everything from demand forecasting and inventory management to logistics and supplier coordination. Studies show that high digital maturity correlates with better operational efficiency, quicker adaptation to disruptions, and stronger customer engagement (EY, 2025).
Figure 1: Journey of Smart Supply Chain Maturity Assessment and Transformation.
Industry-specific models often categorize digital maturity into phases ranging from early adopters of basic automation to highly integrated networks that utilize real-time data for predictive and prescriptive decision-making. At lower levels, companies might rely on siloed IT systems and minimal process automation. As they progress, they begin to adopt more sophisticated technologies—such as AI-driven forecasting or blockchain-based traceability—leading to a fully digitalized state where systems interact seamlessly and provide continuous, actionable insights (PwC, 2024). In emerging markets, the pace of progression can be influenced by constraints like limited IT infrastructure, regulatory environments, or workforce digital literacy. Nevertheless, even modest improvements in digital maturity can yield significant benefits, including heightened transparency, reduced lead times, and cost savings (Deloitte, 2023).
Formal frameworks like the Digital Supply Chain Maturity Model help organizations benchmark their progress and set targeted objectives (KPMG, 2023). These models typically evaluate dimensions such as:
Technology Integration: The scope and sophistication of digital tools, from basic automation (e.g., barcode scanning) to advanced AI and robotics.
Data Management: Data collection, governance, and analytics capabilities that enable real-time, data-driven decisions.
Workforce Readiness: The extent to which employees possess the digital skills needed for efficient tool utilization and innovation.
Organizational Culture: Leadership support, change management, and a culture that fosters experimentation and continuous learning.
Companies like Walmart have employed maturity assessments to map out their technological landscape before rolling out large-scale AI-driven forecasting or blockchain solutions (PwC, 2024). Manufacturing giants such as Siemens, on the other hand, examine both technological and human factors—ranging from machinery readiness to employee skill sets—ensuring that supply chain transformations align with broader operational goals (Deloitte, 2023). In emerging markets, maturity assessments similarly spotlight infrastructure or cultural gaps, guiding investments in areas like upskilling and digital infrastructure.
Digital maturity is not solely a function of infrastructure; workforce capabilities and organizational culture play equally pivotal roles. Even with cutting-edge systems, digital transformation can stall if teams lack the necessary digital literacy or if cultural barriers impede adoption (EY, 2025). Hence, maturity assessments often incorporate surveys, skill audits, and leadership interviews to gauge factors like employee comfort with data analytics, openness to innovation, and the availability of training programs (Chong and Lu, 2022). Results from these assessments illuminate skill gaps that can be addressed through targeted reskilling or the recruitment of digital-savvy talent, thereby anchoring new technologies in an environment conducive to adoption.
Recent advances in AI have given rise to sophisticated tools that evaluate an organization’s digital maturity more granularly. These platforms analyze data from IT infrastructure, workforce capabilities, and existing workflows to produce real-time dashboards on readiness levels across different units (KPMG, 2023). Predictive modeling features further help leaders envision how new technologies—such as IoT sensors for real-time inventory tracking—might perform in practice, enabling proactive adjustments to minimize implementation risks (PwC, 2024).
Digital twin technology, while widely known for operational applications like optimizing logistics or warehouse layouts, is increasingly employed to simulate the broader impact of digital transformations. By creating virtual replicas of supply chain networks, companies can experiment with the integration of tools like blockchain for traceability or advanced robotics without disrupting live operations (Deloitte, 2023). This simulation-based approach is especially valuable in emerging economies, where limited capital may necessitate more cautious pilot programs, as digital twins allow planners to test scenario outcomes and cost implications before executing major changes.
Regardless of regional context, organizations stand to benefit from systematic evaluations of their digital maturity. High-profile adopters in retail, logistics, and manufacturing demonstrate that thorough readiness assessments—covering technology, workforce, and cultural dimensions—provide a roadmap for transformative yet sustainable digitalization (Chong and Lu, 2022). By bridging identified gaps, companies can enhance supply chain resilience, cut operational costs, and elevate customer service. Meanwhile, emerging-market enterprises can utilize these frameworks to leapfrog certain phases of technology adoption, mitigating constraints like sporadic internet connectivity or insufficiently trained personnel (EY, 2025).
Over time, continuous monitoring of digital maturity allows organizations to adapt to evolving business environments, regulatory changes, and technological advancements. Combining advanced analytics with iterative assessment methods ensures that digital transformation efforts remain aligned with strategic objectives—a vital consideration as supply chains grapple with new challenges, from climate-driven disruptions to shifts in global trade patterns (PwC, 2024).
Digital maturity underpins an organization’s capacity to integrate advanced supply chain technologies and realize their full benefits. Through robust maturity assessment models, AI-based evaluation tools, and digital twin simulations, companies can objectively gauge their current readiness, identify strategic investment areas, and ensure that transformation initiatives are executed effectively (KPMG, 2023). Equally important is the alignment of human capital and corporate culture with digital aspirations, ensuring that employees possess the skills and mindset required to capitalize on innovation (Deloitte, 2023). As global enterprises and emerging-market firms alike accelerate their digital transformations, a clear understanding of digital maturity proves indispensable for crafting resilient, data-driven, and future-proof supply chain ecosystems.
10.2. Building a Roadmap for Smart Supply Chains
A digital transformation roadmap provides the strategic foundation for organizations seeking to integrate advanced technologies—such as AI, IoT, and blockchain—into their supply chains, aligning technical innovations with overarching business objectives. In contrast to one-off change initiatives, digital transformation is a continuous process requiring a clear vision, phased goals, and flexible execution plans (KPMG, 2023). By delineating key milestones and balancing short-term gains with long-term strategic growth, a roadmap enables companies to extract tangible value from technology investments and ensure the transformation is both scalable and sustainable (Deloitte, 2023).
Central to any digital transformation roadmap is the focus on value alignment. This concept ensures that digital tools directly serve strategic aims—whether improving operational efficiency, increasing supply chain resilience, or supporting sustainability initiatives (PwC, 2024). Without explicit alignment, investments in cutting-edge technologies risk becoming siloed or duplicative, undermining the overall transformation (Huang and Li, 2021). For example, an organization targeting improved demand forecasting might zero in on AI-powered predictive analytics that integrate seamlessly with existing ERP systems, ensuring immediate operational relevance and measurable ROI.
Figure 2: Developing Roadmap for Digital Transformation of Smart Supply Chains.
Research underscores that businesses yielding lasting benefits from digital transformation typically maintain rigorous alignment between technology deployments and organizational priorities (Huang and Li, 2021). By setting specific, quantifiable targets—such as reducing lead times by 20% or lowering inventory holding costs—companies create a framework for evaluating the success of each roadmap milestone (EY, 2025). This structured approach not only clarifies resource allocation but also keeps cross-functional teams focused on measurable outcomes.
In building a transformation roadmap, three core pillars commonly shape success:
Technology Selection: Identifying suitable platforms or systems is often the first visible step, requiring careful assessment of current infrastructure, future scalability, and potential integration with other supply chain functions (KPMG, 2023). Technologies like AI for predictive analytics, IoT for real-time tracking, and blockchain for transparency must be chosen based on their capacity to advance strategic objectives while remaining adaptable to evolving market conditions (Deloitte, 2023). Emerging market enterprises, for instance, might prioritize low-cost IoT sensor deployments to tackle basic challenges in inventory management before adopting more advanced solutions.
Workforce Development: Digital transformation necessitates a workforce adept at leveraging new tools. Reskilling or upskilling becomes indispensable, especially in regions where digital expertise is limited (PwC, 2024). By offering specialized training programs and collaborating with educational institutions, organizations can cultivate the skills needed to integrate and maintain advanced systems. A robust talent strategy also guards against attrition, ensuring continuity in newly automated processes (Huang and Li, 2021).
Change Management: Introducing new technologies often demands a shift in organizational culture—one that embraces experimentation and iterative learning (EY, 2025). Clear communication regarding transformation goals and anticipated benefits can alleviate employees’ apprehensions, while inclusive decision-making fosters ownership and cooperation (Deloitte, 2023). This cultural shift is equally vital in emerging markets where hierarchical structures may challenge the open collaboration often required in digital projects.
Scholarly work on digital transformation suggests a phased or incremental approach is more likely to yield sustainable outcomes than attempting a comprehensive overhaul at once (Huang and Li, 2021). Early ‘quick wins’—like deploying IoT sensors on a single production line—build confidence and secure organizational buy-in, allowing teams to refine processes before wider rollout. This model is evident in companies like Walmart, which initiated its digital transformation by upgrading core IT infrastructure and then layered on more advanced IoT and AI capabilities incrementally (PwC, 2024). Each stage delivered measurable improvements, cementing cross-functional support and minimizing the risk of disruption.
In manufacturing, Siemens illustrates a similar roadmap. By focusing initially on automation and analytics in selected facilities, Siemens demonstrated tangible benefits, then gradually scaled the solutions across its global network. Concurrently, Siemens invested in workforce development, offering training to ensure employees could fully exploit AI-driven analytics and digital twin simulations (Deloitte, 2023). Such incremental success stories underscore the importance of strategic pacing and methodical expansion, ensuring technology investments remain aligned with business priorities and do not overwhelm organizational capacities.
Technological innovations are increasingly shaping how roadmaps are created and executed. AI-driven project management tools, for instance, use real-time analytics to track transformation progress, predict potential bottlenecks, and recommend corrective actions (KPMG, 2023). These systems automate much of the reporting and data gathering, freeing leaders to focus on strategic decisions rather than administrative tasks. Especially in emerging markets—where project management expertise may be scarce—AI-based tools can streamline cross-functional collaboration and maintain momentum throughout the transformation journey (EY, 2025).
Digital twin technology similarly redefines how organizations plan and test roadmap initiatives. By simulating supply chain scenarios within a virtual model, companies can forecast operational impacts—ranging from warehouse reconfigurations to new logistics routes—without disrupting live operations (PwC, 2024). This approach significantly reduces risk, provides cost estimates, and refines solution designs prior to large-scale implementation (Huang and Li, 2021). For logistics-heavy enterprises, digital twins enable iterative prototyping of route optimizations or fleet reorganizations, ensuring resource investments yield optimal returns.
A carefully devised digital transformation roadmap is essential for organizations endeavoring to create or refine smart supply chains. By focusing on value alignment, methodical technology selection, workforce readiness, and adaptive change management, companies can drive stepwise improvements that culminate in robust, data-driven operations (KPMG, 2023). Examples from industry leaders such as Walmart and Siemens affirm the practicality of a phased approach, supplemented by tools like AI-driven project management and digital twin simulations that mitigate risk while maximizing impact. As global markets evolve and new disruptions arise, a well-maintained roadmap ensures that supply chains remain agile, efficient, and aligned with overarching business objectives (Deloitte, 2023). This holistic approach, balancing near-term operational gains with long-term strategic resilience, is vital for any organization determined to thrive in today’s fast-paced, interconnected world.
10.3. Leveraging Partnerships and Ecosystems
In an era where global supply chains are increasingly complex, partnerships and collaborative ecosystems have become central to the successful implementation of smart supply chains (KPMG, 2023; PwC, 2024). Rather than tackling every aspect of digital transformation independently, organizations forge alliances that allow them to access specialized expertise, share risks, and accelerate technological adoption. Through these strategic partnerships, companies can leverage resources from technology vendors, logistics providers, and data analytics firms, thereby reducing barriers to implementing solutions such as AI, IoT, and blockchain (Deloitte, 2023). This collaborative approach also fosters innovation, enabling rapid experimentation with new tools without incurring prohibitive development costs, a benefit particularly salient for businesses in emerging markets where infrastructure gaps may impede large-scale rollouts (EY, 2025).
Figure 3: Partnerships and Ecosystems Strategies of Smart Supply Chains.
A digital ecosystem stretches beyond the traditional supply chain structure to include a wide array of stakeholders, including software developers, financial institutions, and specialized research bodies (Zhang and Zhou, 2021). This holistic perspective contrasts with the siloed models of the past, promoting shared goals and open data exchange. As a result, partners within the ecosystem can align on common objectives such as sustainability, operational efficiency, or customer satisfaction—amplifying the benefits of each participant’s contributions. In emerging markets, the ecosystem model also broadens market access, allowing small and medium enterprises to tap into global networks, acquire advanced technologies, and elevate service offerings that were previously out of reach (KPMG, 2023).
Scholarly analyses underscore that ecosystems enhance organizational resilience and adaptability by pooling complementary capabilities. Research suggests that the “network effects” generated through alliances reduce redundancy, expedite solutions to shared challenges, and mitigate risks associated with disruptive market forces (Zhang and Zhou, 2021). This capacity for rapid innovation and collective learning stands out as a key advantage of ecosystems in tackling fast-changing supply chain demands.
Amazon’s Logistics Ecosystem: Amazon’s approach exemplifies how a robust partner network underpins one of the world’s most advanced supply chains. By collaborating with regional carriers, third-party delivery providers, and cloud vendors, Amazon extends its geographic coverage and dynamically allocates resources to match evolving customer demands (PwC, 2024). Equally crucial, Amazon’s partnerships facilitate the deployment of data-intensive solutions—ranging from predictive route optimization to warehouse robotics—on a massive scale. This strategic ecosystem ensures that Amazon remains agile, cost-competitive, and capable of delivering on tight service-level commitments worldwide (Deloitte, 2023).
Ford-IBM Blockchain Collaboration: In the automotive sphere, Ford’s alliance with IBM demonstrates how blockchain can be harnessed to improve transparency and ethical sourcing in complex supply chains (KPMG, 2023). By using a decentralized ledger to trace cobalt from mines to production facilities, the partnership mitigates risks tied to counterfeit materials and unethical labor practices. This joint effort underscores how organizations can leverage advanced technologies more effectively by pooling their expertise and infrastructure, with each partner focusing on its core competencies—blockchain development on one side and automotive supply chain management on the other (Zhang and Zhou, 2021).
Siemens’ Digital Enterprise Alliances: Siemens, a leader in manufacturing and industrial automation, has strategically allied with software vendors, IoT providers, and cloud platforms to build an integrated Digital Enterprise ecosystem (EY, 2025). Through these partnerships, Siemens integrates predictive maintenance, digital twins, and AI-driven analytics across its production lines, enhancing scalability and resource allocation. Collaboration also expedites the continuous improvement of Siemens’ offerings, as new innovations and methodologies can be swiftly tested and incorporated, ensuring that its global manufacturing footprint remains state-of-the-art (Deloitte, 2023).
In regions with infrastructural constraints, partnerships often serve as catalysts for digital transformation. In Southeast Asia, for instance, e-commerce players collaborate with local logistics providers, payment gateways, and data analytics firms to establish reliable, cross-border supply chain solutions (PwC, 2024). This synergy allows smaller enterprises to benefit from shared investments in technology platforms, labor training, and route optimization. It also facilitates knowledge transfer, with local firms learning from multinational partners that bring global best practices and technological know-how, enabling emerging markets to integrate into worldwide supply chain networks (EY, 2025).
The proliferation of blockchain technology has substantially reshaped data sharing and trust-building across extended supply chains. By providing a tamper-proof ledger, blockchain eliminates the need for centralized oversight, boosting transparency among partners. Smart contracts further automate compliance checks and transactional milestones, freeing companies to focus on strategic decisions rather than administrative overhead (KPMG, 2023).
Another linchpin of ecosystem collaboration is open APIs, which streamline data exchange by interlinking disparate systems (Zhang and Zhou, 2021). For example, a logistics provider can seamlessly integrate its scheduling platform with a retailer’s inventory database, enabling real-time visibility into stock levels and optimizing delivery routes. This interoperability is crucial in emerging markets where companies may rely on legacy systems but still require modern digital capabilities to compete.
AI-driven forecasting completes the trifecta of ecosystem enablers, providing predictive insights that partners can use to refine demand planning, route allocation, and resource utilization (Deloitte, 2023). By collectively pooling data from manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors, AI systems generate more accurate forecasts than any single entity could on its own. This approach not only reduces the risk of stockouts or waste but also fosters a spirit of cooperation that extends beyond immediate cost savings.
Strategic partnerships and collaborative ecosystems are integral to implementing smart supply chains in a highly competitive, rapidly evolving digital landscape. By allying with technology providers, logistics partners, and other stakeholders, organizations can tap into specialized knowledge, accelerate transformative initiatives, and maintain resilience against market volatility (KPMG, 2023). High-profile alliances, like those exemplified by Amazon, Ford, and Siemens, illustrate the tangible benefits of this approach: optimized operations, rapid scaling of new solutions, and a fertile environment for continuous innovation (PwC, 2024). Emerging technologies such as blockchain, open APIs, and AI-based forecasting reinforce these ecosystems by facilitating secure data exchange, interoperability, and real-time analytics (Deloitte, 2023). For businesses across both advanced and emerging markets, embracing partnerships and ecosystems paves the way for agile, scalable, and future-ready supply chains capable of thriving in an era defined by digital disruption (EY, 2025).
10.4. Key Metrics and KPIs in Smart Supply Chain Execution
The accelerated pace of digital transformation in global supply chains underscores the importance of robust metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). These KPIs facilitate data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement, particularly in complex operations that rely on AI, IoT, and cloud-based analytics (KPMG, 2023; PwC, 2024). Unlike traditional metrics, smart supply chain KPIs must reflect the interconnected nature of digitally enhanced workflows, capturing real-time data and aligning closely with overarching business strategies. By setting well-defined KPIs that mirror objectives around efficiency, cost reduction, sustainability, and customer satisfaction, organizations can monitor progress, identify inefficiencies, and pivot quickly when market conditions shift (Deloitte, 2023).
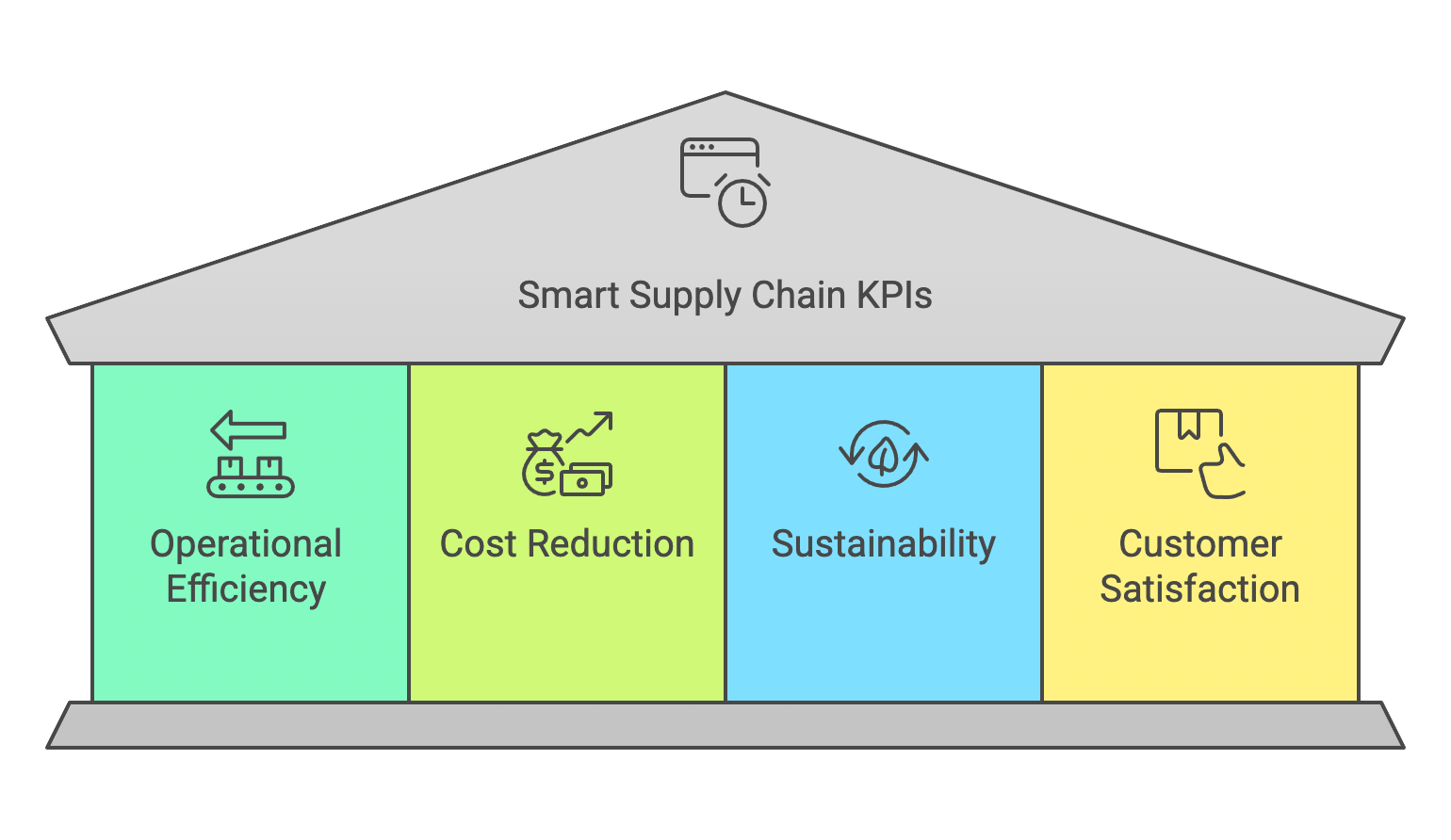
Figure 4: Recommendation for Smart Supply Chain KPIs.
Effective KPIs help companies ensure that each element of their supply chain transformation meets clear, quantifiable targets. From reducing lead times to enhancing environmental sustainability, KPIs serve as reference points for gauging operational success (EY, 2025). Research indicates that frequent measurement and feedback loops—a core aspect of Total Quality Management (TQM)—are equally critical in digital supply chains (Chen, Li, and Sun, 2021). For instance, if a firm’s strategic priority is to boost sustainability, KPIs could track carbon emissions, energy consumption, and recyclable packaging rates, ensuring that environmental gains remain at the forefront of decision-making.
KPIs in a digitally transformed supply chain typically span four key dimensions:
Operational Efficiency: Metrics such as order fulfillment accuracy, inventory turnover, and workflow cycle times gauge how effectively new technologies—like automated picking systems or predictive analytics—streamline processes (PwC, 2024).
Cost Reduction: Analyzing metrics related to logistics expenditures, labor costs, or downtime helps reveal the ROI of automation and AI-driven solutions (Deloitte, 2023).
Sustainability: Environmental KPIs capture reductions in carbon footprint, energy usage, and waste, ensuring that digital enhancements contribute to broader ESG commitments (KPMG, 2023).
Customer Satisfaction: In a landscape where consumers expect rapid, transparent service, KPIs around on-time delivery, responsiveness, and order accuracy become paramount (EY, 2025).
Academic literature stresses that KPIs must remain adaptive, evolving alongside technology maturity and strategic pivots (Chen, Li, and Sun, 2021). For emerging markets, adopting internationally recognized KPI standards can bolster credibility and increase competitiveness in global supply chain networks.
UPS’s Real-Time Efficiency Metrics: UPS leverages an extensive sensor network and real-time analytics to optimize route planning, package sorting, and vehicle utilization (PwC, 2024). Core KPIs include delivery time variance, fuel efficiency, and route optimization scores. By using predictive modeling, UPS anticipates traffic congestion or weather disruptions and reroutes accordingly, cutting both operational costs and carbon emissions. This data-driven monitoring underpins continuous performance improvements, illustrating how well-designed KPIs can boost both profitability and sustainability (KPMG, 2023).
Zara’s Fast Fashion KPIs: Zara’s strength lies in its rapid response to shifting consumer tastes, enabled by finely tuned KPIs that measure lead times, stock turnover, and store replenishment frequencies (Deloitte, 2023). Real-time inventory data allows Zara to dynamically adjust production and distribution, mitigating the risk of overstock or missed sales opportunities. This agile approach to KPI tracking supports Zara’s reputation for quick product refreshes and closely aligns supply with demand—an advantage that anchors the brand’s profitability in a fiercely competitive sector.
Companies across industries increasingly rely on AI-driven analytics platforms to interpret supply chain data, detect anomalies, and surface improvement opportunities (EY, 2025). By aggregating data from IoT devices, ERP systems, and external inputs—such as weather forecasts or social media trends—these platforms provide contextualized insights. For instance, an AI tool might highlight inefficiencies in a warehouse picking process or predict demand spikes that warrant expedited production schedules. This proactive approach prevents costly disruptions and refines KPI targets over time (Chen, Li, and Sun, 2021).
Digital twins offer an additional frontier for KPI monitoring, creating virtual models of physical supply chain assets or processes. By simulating scenarios such as automation rollouts or new route configurations, companies can assess potential KPI gains—like faster delivery times or lower energy consumption—before implementing changes in the real world (KPMG, 2023). Real-time feedback loops between the digital twin and actual operations facilitate iterative optimization, making it easier to maintain consistently high performance metrics.
In regions with developing infrastructure, real-time KPI tracking can yield transformative benefits. AI-driven dashboards and low-cost IoT sensors help local logistics providers pinpoint bottlenecks, reduce delays, and meet global service-level expectations (Deloitte, 2023). Adopting standardized KPIs aligned with international frameworks also positions these companies for cross-border partnerships, as multinational firms often require comparable metrics to evaluate supplier performance (PwC, 2024). Through comprehensive KPI frameworks, emerging market enterprises can progressively enhance reliability, sustainability, and competitiveness, forging an equal footing with established players.
Implementing the right KPIs and metrics is indispensable for organizations striving to validate the impact of smart supply chain transformations. By focusing on operational efficiency, cost savings, sustainability, and customer satisfaction, these metrics guide both day-to-day decisions and long-term strategic planning (KPMG, 2023). Real-world applications from UPS and Zara showcase how continuous monitoring, real-time data analytics, and AI-driven dashboards can elevate supply chain performance. Meanwhile, advanced tools like digital twins enable proactive scenario testing, fostering an environment of sustained improvement (Deloitte, 2023). As both developed and emerging markets integrate digital solutions into their supply chains, well-crafted KPI frameworks will remain central to achieving resilience, adaptability, and sustained competitive advantage (EY, 2025).
10.5. Best Practices for Scaling and Sustaining Smart Supply Chains
Scaling smart supply chain initiatives demands a strategic mindset that balances efficiency with flexibility, ensuring that technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain can extend seamlessly across various operational layers and geographic regions (KPMG, 2023; PwC, 2024). Many organizations begin with successful pilot projects, only to discover that replicating these successes on a broader scale requires rethinking processes, refining technology integrations, and actively cultivating agile, learning-based cultures (Deloitte, 2023). Equally critical is the ability to adapt these innovations to local market conditions, regulatory environments, and infrastructure levels. Without careful planning and continuous improvement, even the most promising supply chain transformations risk stagnation or misalignment with the evolving demands of global commerce (EY, 2025).
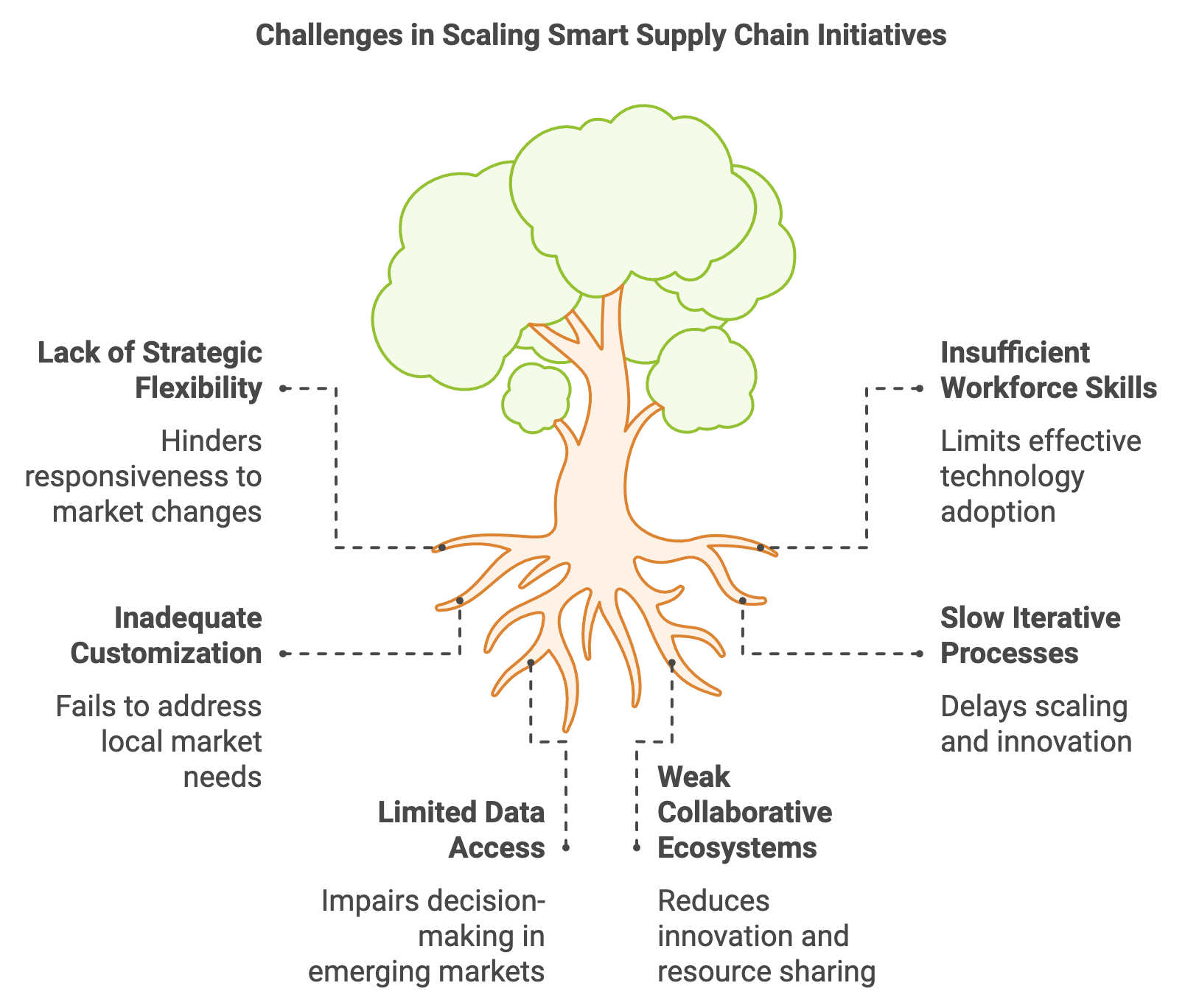
Figure 5: Key challenges in scaling Smart Supply Chains.
Sustaining long-term competitiveness in a smart supply chain environment involves more than implementing cutting-edge solutions; it requires continuous innovation at both technological and organizational levels (Gao, Chen, and Xie, 2022). This ongoing effort entails revisiting and refining deployed systems, upgrading workforce capabilities, and embedding a mindset that prioritizes experimentation and swift adaptation to new challenges (Deloitte, 2023). Research draws on concepts of organizational learning and knowledge management, suggesting that iterative feedback loops—where lessons from each deployment phase inform subsequent adjustments—foster resilience and responsiveness (KPMG, 2023). For businesses in emerging markets with limited digital infrastructure, investing in employee training and agile leadership ensures that talent gaps do not impede the scaling of smart supply chain projects (EY, 2025).
Tesla’s Agile Approach to Global Scaling: Tesla’s success in scaling its manufacturing and supply chain operations illustrates the importance of agility and vertical integration. By using advanced robotics, AI-driven forecasting, and data-centric inventory management, Tesla achieves rapid iteration in production processes, enabling it to align supply closely with fluctuating market demand (PwC, 2024). Moreover, Tesla adopts a phased rollout strategy: technologies proven effective in pilot facilities are carefully adapted to new production lines or global sites based on local requirements. This approach minimizes deployment risks, allows continuous learning, and leverages Tesla’s centralized control over critical supply chain nodes—ranging from battery production to final vehicle assembly (Deloitte, 2023).
P&G’s Modular Deployment and Continuous Learning: Procter & Gamble (P&G) exemplifies how large consumer goods companies can maintain adaptability by using modular deployments and fostering a collaborative culture of ongoing improvement (Gao, Chen, and Xie, 2022). Through real-time digital platforms, P&G monitors supply chain performance across diverse markets, swiftly adjusting to disruptions or surges in consumer demand (KPMG, 2023). The company’s phased rollouts ensure that each digital solution—be it AI for demand forecasting or automated picking—undergoes incremental refinement. This modular approach capitalizes on lessons gleaned from one region or product line, which are then shared with other divisions, reinforcing a global network of best practices (EY, 2025).
Adopting agile methodologies has emerged as a best practice for scaling smart supply chains (Deloitte, 2023). Under this model, organizations deploy new technologies or processes in incremental phases, gather feedback, and refine solutions before broadening their scope. For instance, a company looking to roll out an IoT-enabled tracking system might start with one distribution center, analyze performance data, and resolve any issues prior to implementing the system at other facilities. Such a staged approach reduces both financial and operational risks while enabling early wins that reinforce organizational buy-in. This is particularly relevant in emerging markets where infrastructure constraints, regulatory variances, or workforce skill shortages can complicate large-scale deployments (PwC, 2024).
Predictive analytics and machine learning solutions significantly mitigate the uncertainties of scaling. By analyzing operational data from pilot phases, AI algorithms can forecast potential bottlenecks—such as seasonal demand spikes or supply disruptions—allowing companies to proactively adjust their strategies (KPMG, 2023). Machine learning models continuously refine their predictions based on new data, supporting ongoing performance optimization and cross-site knowledge transfer. This capability is especially useful in contexts with diverse market conditions, such as multinational supply chains or emerging economies.
Sustaining large-scale deployments also benefits from ecosystem-driven innovation. Cloud-based platforms such as SAP’s Ariba Network or IBM’s Sterling Supply Chain Suite enable technology providers, logistics firms, and suppliers to collaborate in an integrated environment (EY, 2025). Companies can co-develop or share best-practice solutions, facilitating a cycle of continual improvement even after initial deployments. For instance, a manufacturer eager to expand digital twins throughout its global footprint can turn to these ecosystems for specialized insights, new integrations, and rapid troubleshooting. In emerging economies, such partnerships mitigate resource limitations by providing access to advanced tools, analytics expertise, and established operational blueprints (Deloitte, 2023).
Cloud-based tools like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), or Google Cloud supply the scalable infrastructure required for data exchange, real-time analytics, and iterative testing (PwC, 2024). These platforms help maintain momentum across distributed teams, support remote collaboration, and offer on-demand computing resources. By simulating expansions of warehouse automation systems or new routing algorithms, supply chain teams can explore multiple scenarios without incurring major capital outlays for infrastructure.
Digital twins not only offer predictive diagnostics but also enable scenario-based planning to test the scalability of solutions (Gao, Chen, and Xie, 2022). A logistics firm might use a digital twin of its transportation network to visualize different configurations of hubs and routes, analyzing cost and efficiency impacts as the company expands regionally or globally. This approach reduces risk by identifying choke points or resource shortages before they materialize in real-world settings.
Scaling and sustaining smart supply chain initiatives entails a multifaceted strategy that integrates flexibility, iterative learning, and cross-functional collaboration (KPMG, 2023). Organizations like Tesla and Procter & Gamble exemplify the success of agile methodologies, modular rollouts, and a culture of continuous improvement in driving innovation at scale (Deloitte, 2023). Meanwhile, AI-driven predictive analytics, collaborative innovation ecosystems, and advanced platforms like digital twins furnish the technological backbone for managing expansions and ensuring consistent performance in diverse environments (PwC, 2024). For companies in emerging as well as developed markets, these best practices underscore the importance of balancing bold innovation with structured execution, securing both near-term efficiency gains and long-term resilience in an ever-evolving global supply chain landscape (EY, 2025).
10.6. Conclusion and Further Learning
In conclusion, implementing and scaling smart supply chains requires a strategic approach that balances technological adoption with a clear roadmap, strong partnerships, and continuous performance measurement. By assessing digital readiness and leveraging advanced tools such as AI, blockchain, and cloud platforms, companies can not only enhance efficiency but also build resilient and adaptable supply chain ecosystems. As businesses move forward, scaling and sustaining innovation through collaboration, agile methodologies, and performance tracking will be essential for long-term success in a rapidly changing global landscape.
Embarking on the journey to implement and scale smart supply chains requires curiosity, strategic thinking, and a commitment to continuous learning. These prompts will help you explore the critical factors that influence digital transformation, the role of partnerships and ecosystems, and the importance of real-time data analytics.
How can companies comprehensively assess their digital maturity and readiness for adopting smart supply chain technologies, considering factors such as existing infrastructure, organizational culture, workforce capabilities, and strategic alignment, and what frameworks or models are most effective for this assessment?
What are the key stages of the Digital Supply Chain Maturity Model, from foundational adoption to advanced digital integration, and how can organizations accurately determine their position on this scale while identifying actionable steps to advance to higher maturity levels?
How can AI-driven tools and platforms assist businesses in conducting an in-depth evaluation of their technological capabilities, identifying gaps in digital readiness, and developing strategies to close those gaps, particularly in areas such as automation, data integration, and workforce adaptability?
What are the essential components of a comprehensive digital transformation roadmap for supply chains, including technology selection, process optimization, change management, and workforce development, and how can organizations ensure these initiatives align with long-term business goals and sustainability objectives?
What role do cloud-based platforms play in enabling seamless cross-functional collaboration during the digital transformation of supply chains, particularly in real-time data sharing, process integration, and project management across global teams and partners?
How can companies effectively select the right technologies to support their digital supply chain transformation, considering factors such as scalability, interoperability, cost-efficiency, and alignment with business strategy, and what frameworks can guide these decisions to ensure long-term success?
How do strategic partnerships with technology vendors, logistics providers, and cloud service platforms accelerate the implementation of smart supply chains, and what best practices can businesses adopt to leverage these partnerships for innovation, speed to market, and competitive advantage?
What are the key benefits of joining a digital supply chain ecosystem, including enhanced collaboration, innovation, and access to shared resources, and how can businesses foster cross-industry partnerships to drive scalability, agility, and digital transformation across the entire supply chain network?
How can blockchain technology be leveraged to enable secure, transparent collaboration across global supply chain ecosystems, and what are the most promising use cases for blockchain in enhancing traceability, verifying transactions, and preventing fraud in multi-stakeholder environments?
What are the most important KPIs for measuring the success of a smart supply chain implementation, particularly in areas like operational efficiency, cost reduction, sustainability, and customer satisfaction, and how can companies develop real-time tracking systems to monitor these metrics continuously?
How can AI-driven analytics platforms assist organizations in optimizing key supply chain KPIs, making data-driven decisions, and identifying trends or anomalies that impact performance, and what role does predictive analytics play in proactively addressing potential issues before they escalate?
What role do digital twins play in monitoring, simulating, and optimizing supply chain performance, and how can businesses integrate digital twin technology into their operations for continuous improvement, real-time decision-making, and proactive risk management?
What are the best practices for scaling smart supply chain initiatives while maintaining operational flexibility, responsiveness to market changes, and the ability to quickly adapt to new technologies or disruptions in the global supply chain landscape?
How can AI and machine learning technologies be used to predict future challenges and opportunities in scaling smart supply chain innovations, and how can businesses leverage these insights to make proactive decisions, mitigate risks, and capitalize on emerging trends in the industry?
How can companies foster a culture of continuous innovation and improvement in supply chain management, ensuring that new ideas, technologies, and processes are regularly tested, adopted, and refined to sustain long-term competitiveness in an ever-evolving market?
How do agile methodologies and adaptive strategies contribute to the successful scaling of smart supply chain systems globally, and what role do iterative improvements, real-time feedback loops, and cross-functional collaboration play in maintaining a competitive edge?
How can businesses ensure that their supply chain innovations are both sustainable and resilient, addressing global challenges such as climate change, regulatory compliance, and economic volatility, while building flexible, adaptive supply chain systems that can withstand future disruptions?
What role do open APIs and standardized data-sharing protocols play in integrating third-party tools, platforms, and services into smart supply chain systems, and how can businesses ensure seamless interoperability and data flow across complex, multi-vendor ecosystems?
How can real-time data analytics drive more informed decision-making in scaling smart supply chains, particularly in the areas of demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics optimization, and what technologies are essential for real-time visibility and actionable insights?
What are the most common challenges organizations face when scaling their smart supply chain initiatives, including resistance to change, integration issues, and talent shortages, and how can businesses develop strategies to overcome these challenges and successfully scale their digital transformation efforts?
By engaging with these questions, you will deepen your understanding of the advanced technologies, best practices, and innovation strategies that drive successful supply chain management. Let these prompts challenge your thinking and inspire you to embrace the future of smart supply chains with confidence and creativity.
Comments